| Audit Software (Web And PDA): The foAudits toolset provides the software for energy audits, surveys of any kind and typical contractor-related tools such as punch-lists and work orders. foAudits runs on Pocket PCs, the Palm OS, phones and/or the web. See our site for more information. |
| Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp / Systems Engineering Operations : Provider of systems studies, custom applications software programming, contract hardware manufacturing and software research and analysis services. The company specializes in modeling and simulation software, pointing and tracking systems and p.. |
| Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) Simulation Research Group: Specialize in creating building energy simulation software. Building Energy Simulation Programs: DOE-2, EnergyPlus, and SPARK. / (added 09/2005) |
| Building For Environmental And Economic Sustainability : Software from the Building and Fire Research Laboratory, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). |
| CANMET Energy Diversification Research Laboratorys RET: Screen Renewable Energy Project Analysis Software |
| NEW Community for Energy, Environment and Development : This is the home site of a software tool I develop called LEAP: the Long-range Energy Alternatives Planning system. This is a windows based software tool for integrated energy & environmental scenario analysis and climate change mitigation assessment. Licenses to use the system are free to those in developing countries. The software, user guide and training materials are all available for download on the web site. |
| Energy And Environmental Data (DK): makers of WindPro® / (added 09/2005) |
| ENERGY STAR® For Business : A set of software programs developed by EPA including: QuikPlan (building upgrades), QuikChill (chiller plant upgrades), QuikFan (variable air volume upgrades), ProjectKalc (lighting upgrades) and EPA Refrigerator Analysis Program, allow users to plan, manage, track, and report energy-efficiency upgrades in their facilities. Results include energy and economic analysis of the upgrades. Online tools are provided for developing, tracking, and evaluating your organization’s approach to reducing energy costs over time and comparing your buildings’ energy performance to that of similar buildings throughout the US. Online registration is required to download the software. |
| Fundamental Objects Inc : FO specializes in handheld development, including integration with your existing database or web site. / (added 09/2005) |
| Hybrid Optimization Model For Electric Renewables (HOMER): is used for designing standalone electric power systems that employ some combination of wind turbines, photovoltaic panels, or diesel generators to produce electricity. |
| Maui Solar Energy Software : Provider of the Solar Design Studio v4.0 CD-ROM that contains a suite of Windows 95, 98 and NT software designed to simulate photovoltaic energy system operation. / (added 09/2005) |
| Resoft Ltd – Wind Energy Software : WindFarm enables you to analyze, design and optimize your proposed wind farm. User friendly and powerful, WindFarm runs under Windows 95/98/NT/2000 and XP and does not require any external software packages. It will significantly enhance your wind farm development potential and is fully supported with extensive documentation and help system. |
| Retscreen International Renewable Energy Project Analysis Software: Free software provided by Canada to evaluate renewable energy projects. Evaluate the energy production, life-cycle costs, and greenhouse gas emissions reduction for central-grid and isolated-grid connected small hydro projects. |
 admin1
admin1
DSE Energy Glossary
| Sacrificial Anode | A piece of metal buried near a structure that is to be protected from corrosion. The metal of the sacrificial anode is intended to corrode and reduce the corrosion of the protected structure. |
| Sae Viscosity Number | A system established by the Society of Automotive Engineers for classifying crankcase oils and automotive transmission and differential lubricants according to their viscosities. |
| Santa Ana Winds | Hot winds that emerge from the Great Basin between the Sierras and the Rocky Mountains. It blows into the Los Angeles basin of California, often at speeds over 100 kilometers per hour. It dries out vegetation, causing serious fire danger. |
| Satellite Power System (Sps) | Concept for providing large amounts of electricity for use on the Earth from one or more satellites in geosynchronous Earth orbit. A very large array of solar cells on each satellite would provide electricity, which would be converted to microwave energy and beamed to a receiving antenna on the ground. There, it would be reconverted into electricity and distributed the same as any other centrally generated power, through a grid. |
| Scheduling Coordinator | Scheduling coordinators (SCs) submit balanced schedules and provide settlement-ready meter data to the ISO. |
| Schottky Barrier | A cell barrier established as the interface between a semiconductor, such as silicon, and a sheet of metal. |
| Scribing | The cutting of a grid pattern of grooves in a semiconductor material, generally for the purpose of making interconnections. |
| Sealed Battery | A battery with a captive electrolyte and a re-sealing vent cap to which electrolyte cannot be added. Also called a valve-regulated battery. |
| Sealed Lead Acid Battery | A form of lead acid battery where the electrolyte is immobilized. |
| Sealed Lead-Acid Battery | A form of lead-acid battery where the electrolyte is immobilized, either by being contained in an absorbent fibre separator or gel between the batteries plates. |
| Seasonal Depth Of Discharge | An adjustment factor used in some system sizing procedures which "allows" the battery to be gradually discharged over a 30-90 day period of poor solar insolation. This factor results in a slightly smaller photovoltaic array. |
| Secondary Battery | A battery that can be recharged. |
| Secondary Cell | Secondary cells are batteries (electrochemical cells) that are rechargeable. The chemical reaction within the secondary cell is reversible, allowing the cell to be recharged many times. |
| Secondary Energy | See NON-FIRM ENERGY. |
| Securitize | The aggregation of contracts for the purchase of the power output from various energy projects into one pool which then offers shares for sale in the investment market. This strategy diversifies project risks from what they would be if each project were financed individually, thereby reducing the cost of financing. Fannie Mae performs such a function in the home mortgage market. |
| Seer (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) | the total cooling output of a central air conditioning unit in Btus during its normal usage period for cooling divided by the total electrical energy input in watt-hours during the same period, as determined using specified federal test procedures. (Title 20, Section 2-1602(c)(11). |
| Self Discharge | Self discharge represents energy lost to internal chemical reactions within the cell. |
| Self Discharge Rate | The rate at which a battery will lose its charge when at open circuit (with no load connected). |
| Self-Discharge | The rate at which a battery, without a load, will lose its charge. |
| Self-Generation | A generation facility dedicated to serving a particular retail customer,usually located on the customer’s premises. The facility may either be owned directly by the retail customer or owned by a third party with a contractual arrangement to provide electricity to meet some or all of the customer’s load. |
| Self-Service Wheeling | Primarily an accounting policy comparable to net-billing or running the meter backwards. An entity owns generation that produces excess electricity at one site, that is used at another site(s) owned by the same entity. It is given billing credit for the excess electricity (displacing retail electricity costs minus wheeling charges) on the bills for its other sites. |
| Semiconductor | A material that has an electrical conductivity in between that of a metal and an insulator. |
| Semicrystalline | See Multicrystalline. |
| Sensible Cooling Capacity | See COOLING CAPACITY, SENSIBLE. |
| Sensible Heat | Heat that results in a temperature change. |
| Sensor (Temperature) | Sensing device that changes its electrical resistance according to temperature. Used in the control system of a solar thermal system to measure collector and storage tank temperatures. |
| Series Connected | A method of connection in which the positive terminal of one device is connected to the negative terminal of another. The voltages add and the current is limited to the least of any device in the string. |
| Series Connection | A way of joining photovoltaic cells by connecting positive leads to negative leads; such a configuration increases the voltage. |
| Series Controller | A charge controller that interrupts the charging current by open-circuiting the photovoltaic (PV) array. The control element is in series with the PV array and battery. |
| Series Regulator | A device that prevents overcharging of a battery by disconnecting the charging source as the battery voltage approaches some upper limit. |
| Series Resistance | Parasitic resistance to current flow in a cell due to mechanisms such as resistance from the bulk of the semiconductor material, metallic contacts, and interconnections. |
| Series String | A group of PV modules or batteries wired in series. |
| Series Wiring | A system of wiring for PV panels that increases the current. |
| Service Area | any contiguous geographic area serviced by the same electric utility. |
| Set Point | Scheduled operating level for each generating unit or other resource scheduled to run in the Hour-ahead Schedule. |
| Setback Thermostat | See THERMOSTAT, SETBACK. |
| Settlement | The process of financial settlement for products and services purchased and sold. Each settlement involves a price and quantity. Both the ISO and PX may perform settlement functions. |
| Shade Screen | A screen affixed to the exterior of a window or other glazed opening, designed to reduce the solar radiation reaching the glazing. |
| Shading Coefficient | the ratio of solar heat gain through a specific glazing system to the total solar heat gain through a single layer of clear, double-strength glass. |
| Shallow Cycle Battery | A battery with small plates that can not withstand many deep discharges. |
| Shallow-Cycle Battery | A battery with small plates that cannot withstand many deep discharges (i.e. To a low state of charge). |
| Shelf Life | The amount of time a device, such as battery, can be stored and still retain its specified performance. |
| Shelf Life Of Batteries | The length of time, under specified conditions, that a battery can be stored so that it keeps its guaranteed capacity. |
| Short Circuit | A circuit in which two source leads of opposite polarity or dissimilar potential are connected directly to each other with no regulation or load in between, allowing the full energy potential of the source to flow through the circuit. A short circuit will trip the breaker or fuse, and may damage components, or even cause a fire. |
| Short Circuit Current (ISC) | The current between two points in a circuit when the points are electrically connected with a conductor with essentially zero resistance. Normally applied to PV modules, which can be short circuited safely because they are limited current devices. |
| SHUNT (Noun) | 1. A resistive load through which electron flow is diverted, typically used to heat air or water. 2. A component with a precise, known resistance used to determine amperage by measuring the voltage across it and using Ohm’s law (I = V/R). |
| SHUNT (Verb) | To divert electrical current to a separate circuit or load. |
| Shunt Controller | A charge controller that redirects or shunts the charging current away from the battery. The controller requires a large heat sink to dissipate the current from the short-circuited photovoltaic array. Most shunt controllers are for smaller systems producing 30 amperes or less. |
| Shunt Regulator | A device that prevents overcharging of a battery by diverting some (or all) of the charging current to a resistive load when the battery voltage reaches a preset upper limit. |
| Side Fins | Vertical shading elements mounted on either side of a glazed opening that blocks direct solar radiation from the lower, lateral portions of the sun’s path. SITE |
| Side-Of-Pole Mount | A PV mount installed on the side of a pole. May be fixed or seasonally adjustable. |
| Siemens Process | A commercial method of making purified silicon. |
| Silicon | A nonmetallic element, which when specially treated, is sensitive to light and capable of transforming light into electricity. Silicon is the basic material of most beach sand, and is the raw material used to manufacture most photovoltaic cells. |
| Silicon (Si) | A chemical element with atomic number 14, a dark gray semi-metal. Occurs in a wide range of silicate minerals and makes up approximately 28% of the earth’s crust (by weight). Silicon has a face-centered cubic lattice structure like diamond. The most common semiconductor material used in making PV cells either traditionally in its crystalline form or more recently as an amorphous thin film. |
| Simoom | The searing �poison wind� of Arabia, which roars across the parched desert, sometimes reaching temperatures of 130 degrees Fahrenheit. |
| Sine Wave | A waveform corresponding to a single-frequency periodic oscillation that can be mathematically represented as a function of amplitude versus angle in which the value of the curve at any point is equal to the sine of that angle. |
| Sine Wave Inverter | An inverter that produces grid-quality, sine wave AC electricity. |
| Single Crystal Cell | A wafer of silicon that has a perfect, continuous, crystal lattice (on the atomic level). |
| Single-Crystal Material | A material that is composed of a single crystal or a few large crystals. |
| Single-Crystal Silicon | Material with a single crystalline formation. Many photovoltaic cells are made from single-crystal silicon. |
| Single-Stage Controller | A charge controller that redirects all charging current as the battery nears full state-of-charge. |
| Sirocco | The blistering winds of the Sahara, which blow dust, grit, and sand all the way from northern Africa across the Mediterranean Sea to Europe. |
| Site Energy | The energy consumed at a building location or other end-use site. SKYLIGHT |
| Site Evaluation | An estimation of a location for its potential for solar, hydro, or wind power. |
| Sky Temperature | The equivalent temperature of the clouds, water vapor, and other atmospheric elements that make up the sky to which a surface can radiate heat. |
| Slip Ring | Used to transfer electricity to or from rotating parts in motors and yaw mechanisms. |
| Smog | Originally "smog" meant a mixture of smoke and fog. The definition has expanded to mean air that has restricted visibility due to pollution. Pollution formed in the presence of sunlight is called photochemical smog. According to the U.S. EPA, smog is "a mixture of pollutants, principally ground-level ozone, produced by chemical reactions in the air involving smog-forming chemicals. A major portion of smog-formers come from burning of petroleum-based fuels such as gasoline. Other smog-formers, volatile organic compounds, are found in products such as paints and solvents. Smog can harm health, damage the environment and cause poor visibility. Major smog occurrences are often linked to heavy motor vehicle traffic, sunshine, high temperatures and calm winds or temperature inversion (weather condition in which warm air is trapped close to the ground instead of rising). Smog is often worse away from the source of the smog-forming chemicals, since the chemical reactions that result in smog occur in the sky while the reacting chemicals are being blown away from their sources by winds." |
| Socket | A hollow opening or cavity into which something fits, such as an electric light socket. |
| Solar Cell | see photovoltaic (PV) cell. |
| Solar Collector | A component of an active or passive solar system that absorbs solar radiation to heat a transfer medium which, in turn, supplies heat energy to the space or water heating system. |
| Solar Constant | The average amount of solar radiation that reaches the earth’s upper atmosphere on a surface perpendicular to the sun’s rays; equal to 1353 Watts per square meter or 492 Btu per square foot. |
| Solar Cooker | A device that converts the sun’s energy into heat energy, which is then used to cook food. |
| Solar Cooling | The use of solar thermal energy or solar electricity to power a cooling appliance. Photovoltaic systems can power evaporative coolers ("swamp" coolers), heat-pumps, and air conditioners. |
| Solar Energy | Electromagnetic energy transmitted from the sun (solar radiation). |
| Solar Energy Research Institute (Seri) | Established in 1974 and funded by the federal government, the institute’s general purpose is to support U.S. Department of Energy’s solar energy program and foster the widespread use of all aspects of solar technology, including photovoltaics, solar heating and cooling, solar thermal power generation, wind ocean thermal conversion and biomass conversion. |
| Solar Heat Gain | Heat added to a space due to transmitted and absorbed solar energy. |
| Solar Heat Gain Factor | An estimate used in calculating cooling loads of the heat gain due to transmitted and absorbed solar energy through 1/8"-thick, clear glass at a specific latitude, time and orientation. |
| Solar Heating And Hot Water Systems | Solar heating or hot water systems provide two basic functions: (a) capturing the sun’s radiant energy, converting it into heat energy, and storing this heat in insulated storage tank(s); and (b) delivering the stored energy as needed to either the domestic hot water or heating system. These components are called the collection and delivery subsystems. |
| Solar Insolation | See insolation. |
| Solar Irradiance | See irradiance. |
| Solar Irradiation | The amount of radiation, both direct and diffuse, that can be received at any given location. |
| Solar Module | A device used to convert light from the sun directly into DC electricity by using the photovoltaic effect. Usually made of multiple solar cells bonded between glass and a backing material. A typical Solar Module would be 100 Watts of power output (but module powers can range from 1 Watt to 300 Watts) and have dimensions of 2 feet by 4 feet. |
| Solar Noon | The midpoint between sunrise and sunset, the time when it reaches it’s highest point. |
| Solar Panel | See photovoltaic (PV) panel. |
| Solar Power | Electricity generated by conversion of sunlight, either directly through the use of photovoltaic panels, or indirectly through solar-thermal processes. |
| Solar Radiation | Electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. |
| Solar Resource | The amount of solar insolation a site receives, usually measured in kwh/m2/day, which is equivalent to the number of peak sun hours. |
| Solar Satellite Power | A proposed process of using satellites in geosynchronous orbit above the earth to capture solar energy with photovoltaic cells, convert it to microwave energy, beam the microwaves to earth where they would be received by large antennas, and changed from microwave into usable electricity. |
| Solar Spectrum | The total distribution of electromagnetic radiation emanating from the sun. |
| Solar Thermal | A form of power generation using concentrated sunlight to heat water or other fluid that may then used to drive a motor or turbine. |
| Solar Thermal Collectors | A solar collector is a device designed to absorb incident solar radiation and to transfer the energy to the fluid or air passing through it. |
| Solar Thermal Electric | Method of producing electricity from solar energy by using focused sunlight to heat a working fluid, which in turn drives a turbogenerator. |
| Solar Thermal Electric Systems | Solar energy conversion technologies that convert solar energy to electricity, by heating a working fluid to power a turbine that drives a generator. Examples of these systems include central receiver systems, parabolic dish, and solar trough. |
| Solar Thermal Power Plant | means a thermal powerplant in which 75 percent or more of the total energy output is from solar energy and the use of backup fuels, such as oil, natural gas, and coal, does not, in the aggregate, exceed 25 percent of the total energy input of the facility during any calendar year period. |
| Solar Water Heating Systems | heat water, either directly or by heating a �working fluid� that then heats the water. Solar water heaters are commonly used to heat domestic water in homes; heat water for swimming pools, spas and hot tubs (a particularly cost-effective application); or to heat water for industrial processes. |
| Solar-Electric Cell | See PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL |
| Solar-Electric Module | See PHOTOVOLTAIC MODULE |
| Solar-Grade Silicon | Intermediate-grade silicon used in the manufacture of solar cells. Less expensive than electronic-grade silicon. |
| Solid Fuels | Any fuel that is in solid form, such as wood, peat, lignite, coal, and manufactured fuels such as pulverized coal, coke, charcoal briquettes, and pellets. |
| Solstice (Summer & Winter | The longest and shortest days of the year. The longest day (Summer Solstice) is about June 21st in the Northern Hemisphere. The shortest day (Winter Solstice) is about December 21st in the Northern Hemisphere. |
| Source Energy | All the energy used in delivering energy to a site, including power generation and transmission and distribution losses, to perform a specific function, such as space conditioning, lighting, or water heating. Approximately three watts (or 10.239 Btus) of energy is consumed to deliver one watt of usable electricity. |
| Space Charge | See cell barrier. |
| Special Contracts | Any contract that provides a utility service under terms and conditions other than those listed in the utility’s tariffs. For example, an electric utility may enter into an agreement with a large customer to provide electricity at a rate below the tariffed rate in order to prevent the customer from taking advantage of some other option that would result in the loss of the customer’s load. This generally allows that customer to compete more effectively in their product market. |
| Specific Gravity | The ratio of the weight of a solution to the weight of an equal volume of water at a specific temperature. |
| Specific Heat | In English units, the quantity of heat, in Btu, needed to raise the temperature of one pound of material one degree Fahrenheit. |
| Spill Energy | See DUMP. |
| Spinning Reserve | Electric power plant or utility capacity on-line and running at low power in excess of actual load. |
| Split-Spectrum Cell | A compound photovoltaic device in which sunlight is first divided into spectral regions by optical means. Each region is then directed to a different photovoltaic cell optimized for converting that portion of the spectrum into electricity. Such a device achieves significantly greater overall conversion of incident sunlight into electricity. |
| Split-The-Savings (Electric Utility) | The basis for settling economy-energy transactions between utilities. The added costs of the supplier are subtracted from the avoided costs of the buyer, and the difference is evenly divided. |
| Sputtering | A process used to apply photovoltaic semiconductor material to a substrate by a physical vapor deposition process where high-energy ions are used to bombard elemental sources of semiconductor material, which eject vapors of atoms that are then deposited in thin layers on a substrate. |
| Squall | A sudden storm of wind, typically accompanied by rain or snow or sleet. |
| Square Wave | A train of rectangular voltage pulses that alternate between two fixed values for equal lengths of time. |
| Square Wave Inverter | A type of inverter that produces square wave output. It consists of a direct current source, four switches, and the load. The switches are power semiconductors that can carry a large current and withstand a high voltage rating. The switches are turned on and off at a correct sequence, at a certain frequency. |
| Staebler-Wronski Effect | The tendency of the sunlight to electricity conversion efficiency of amorphous silicon photovoltaic devices to degrade (drop) upon initial exposure to light. |
| Stand-Alone (PV System) | A solar PV system that operates without connection to a grid a supply of electricity. |
| Stand-Alone System | A system that operates independently of the utility lines. It may draw supplementary electricity from the utility, but is not capable of providing electricity to the utility. |
| Standard Reporting Conditions (Src) | A fixed set of conditions (including meteorological) to which the electrical performance data of a photovoltaic module are translated from the set of actual test conditions. |
| Standard Test Conditions (STC) | Conditions under which a module is typically tested in a laboratory (1) Irradiance intensity of 1000 W/square meter (0.645 watts per square inch), AM1.5 solar reference spectrum, and (3) a cell (module) temperature of 25 degrees C, plus or minus 2 degrees C (77 degrees F, plus or minus 3.6 degrees F). [IEC 1215] |
| Standby Current | The current used by an inverter when no load is active. |
| Standby Loss | A measure of the losses from a water heater tank. When expressed as a percentage, standby loss is the ratio of heat loss per hour to the heat content of the stored water above room temperature. When expressed in watts, standby loss is the heat lost per hour, per square foot of tank surface area. |
| Stand-Off Mounting | Technique for mounting a photovoltaic array on a sloped roof, which involves mounting the modules a short distance above the pitched roof and tilting them to the optimum angle. |
| Start-Up | When the generator has enough rotation to begin producing power. |
| Starved Electrolyte Cell | A battery containing little or no free fluid electrolyte. |
| State Of Charge (Soc) | A ratio, expressed in percent, of the energy remaining in a battery in relation to its capacity when fully charged. |
| State-Of-Charge (SOC) | The available capacity remaining in the battery, expressed as a percentage of the rated capacity. |
| Static Electricity | A type of electrical charge that can build up when two objects rub together. Friction removes some electrons from one object and deposits them on the other. |
| Static Head | The height of the water level above the point of free discharge of the water, normally measured when the pump is off. |
| Steady State Efficiency | A performance rating for space heaters; a measure of the percentage of heat from combustion of gas which is transferred to the space being heated under specified steady state conditions. |
| Steam | the vapor form of water that develops when water boils. Steam is made of very tiny heated water particles (molecules) which are bouncing around and bumping into each other at very high speeds. These heated water molecules are also spreading out and expanding in every direction they can. If we confine or trap water in a container, with a pipe as an opening, and heat the water to steam, it will create great pressure in the container and will rush out the pipe with a great deal of force. This force (the "power" of steam) can be put to work turning a turbine connected to an electricity generator. |
| Steam Electric Plant | A power station in which steam is used to turn the turbines that generate electricity. The heat used to make the steam may come from burning fossil fuel, using a controlled nuclear reaction, concentrating the sun’s energy, tapping the earth’s natural heat or capturing industrial waste heat. |
| Step-Up Gearbox | A step-up gearbox increases turbine electricity production in stages by increasing the number of generator revolutions produced by the rotor revolutions. |
| Stirling Engine | An external combustion engine that converts heat into useable mechanical energy (shaftwork) by the heating (expanding) and cooling (contracting) of a captive gas such as helium or hydrogen. |
| Storage | Storing energy in a battery or battery stack. In water pumping, storage can be achieved by pumping water to a storage tank. |
| Storage Battery | A device capable of transforming energy from electric to chemical form and vice versa. The reactions are almost completely reversible. During discharge, chemical energy is converted to electric energy and is consumed in an external circuit or apparatus. |
| Storage Density | The capacity of a battery, in amp-hours compared to its weight. |
| Storage Type Water Heater | A water heater that heats and stores water at a thermostatically controlled temperature for delivery on demand. |
| Stranded Benefits | Public interest programs and goals which could be compromised or abandoned by a restructured electric industry. These potential "stranded benefits" might include: environmental protection, fuel diversity, energy efficiency, low-income ratepayer assistance, and other types of socially beneficial programs. |
| Stranded Costs/Stranded Assets | See embedded Costs Exceeding Market Prices. |
| Strategic Petroleum Reserve | The strategic petroleum reserve consists of government owned and controlled crude oil stockpiles stored at various locations in the Gulf Coast region of the country. These reserves can be drawn down in response to sever oil supply disruptions. The target is to have a reserve of 750 million barrels of oil. Use of the reserve must be authorized by the President of the United States. |
| Stratification | A condition that occurs when the acid concentration varies from top to bottom in the battery electrolyte. Periodic, controlled charging at voltages that produce gassing will mix the electrolyte. See equalization. |
| Straw Bale Construction | A building technique using straw bales for the walls. See POST AND BEAM CONSTRUCTION. |
| String | A number of cells, modules or panels interconnected electrically in series to produce the required operating voltage. |
| STRUCTURAL INSULATED PANELS (Sips) | A no-cavity solid building system of wall and roof panels "sandwiching" polystyrene insulation between an outer and inner sheathing panel (typically oriented strand board (OSB) or metal). |
| Subduction Boundary | one of two types of converging plate boundaries which occurs when one plate plunges under another overriding plate. |
| Substation | A facility at which two or more lines are switched for operational purposes. May include one or more transformers so that some connected lines operate at different nominal voltages to others. |
| Substrate | The physical material upon which a photovoltaic cell is made. Sub-system. Any one of several components in a PV system (i.e., array, controller, batteries, inverter, load). |
| Subsystem | Any one of several components in a photovoltaic system (i.e., array, controller, batteries, inverter, load). |
| Suction Head | The height of pump above the surface of the water source when the pump is located above the water level. |
| Sulfation | A condition that afflicts unused and discharged batteries; large crystals of lead sulfate grow on the plate, instead of the usual tiny crystals, making the battery extremely difficult to recharge. |
| Sulfur Dioxide (So2) | A colorless gas released as a by-product of combusted fossil fuels containing sulfur. The two primary sources of acid rain are sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. |
| Sulfur Oxides (Sox) | pungent, colorless gases (including sulfur dioxide (SO2); formed primarily by the combustion of fossil fuels; may damage the respiratory tract, as well as plants and trees. |
| Sunk Cost | In economics, a sunk cost is a cost that has already been incurred, and therefore cannot be avoided by any strategy going forward. |
| Superconducting Magnetic Energy Storage (Smes) | SMES technology uses the superconducting characteristics of low-temperature materials to produce intense magnetic fields to store energy. It has been proposed as a storage option to support large-scale use of photovoltaics as a means to smooth out fluctuations in power generation. |
| Superconductivity | The abrupt and large increase in electrical conductivity exhibited by some metals as the temperature approaches absolute zero. |
| Superconductor | Used in some electrical equipment. It is a material that when cooled to near absolute zero, has negligable electrical resistance. |
| Superstrate | The covering on the sun side of a PV module, providing protection for the PV materials from impact and environmental degradation while allowing maximum transmission of the appropriate wavelengths of the solar spectrum. |
| Supertandker | A very large ship designed to transport more than 500,000 deadweight tonnage of oil. |
| Supply Bid | A bid into the PX indicating a price at which a seller is prepared to sell energy or ancillary services. |
| Supply-Side | Activities conducted on the utility’s side of the customer meter. Activities designed to supply electric power to customers, rather than meeting load though energy efficiency measures or on-site generation on the customer side of the meter. |
| Surge | 1. An excessive amount of power drawn by an appliance when it is first switched on. |
| Surge Capacity | The ability of an inverter or generator to deliver instantaneous high currents. |
| Surplus | (Electric utility) Excess firm energy available from a utility or region for which there is no market at the established rates. |
| Sustainable | A material or energy source, which if managed carefully, will provide at current levels indefinitely. |
| Sustainable Energy | Energy that takes into account present needs while not compromising the availability of energy or a healthy environment in the future. |
| Sustained Orderly Development | A condition in which a growing and stable market is identified by orders that are placed on a reliable schedule. The orders increase in magnitude as previous deliveries and engineering and field experience lead to further reductions in costs. The reliability of these orders can be projected many years into the future, on the basis of long-term contracts, to minimize market risks and investor exposure. (See also "Commercialization.") |
| Swept Area | The area (in square feet or meters^2) that a wind generator�s rotor (blades) sweep. This is the collector area for a wind generator. The larger the collector, the more energy it will capture. |
| Switch | a common device which breaks an electrical circuit thereby halting the flow electricity through the circuit. |
| Switch-Mode | A form of converting one form of electricity to another by rapidly switching it on and off and feeding it through a transformer to effect a voltage change. |
| SWRTA | The Southwest Regional Transmission Association. a subregional RTG within WRTA, and awaiting FERC approval. |
| Syncrude | Synthetic crude oil made from coal of from oil shale. |
| Synfuel | Synthetic gas or synthetic oil. Fuel that is artificially made as contrasted to that which is found in nature. Synthetic gas made from coal is considered to be more economical and easier to produce than synthetic oil. When natural gas supplies in the earth are being depleted, it is expected that synthetic gas will be able to be used widely as a substitute fuel. |
| Syngas | Synthetic gas make from coal. |
| System | A combination of equipment and/or controls, accessories, interconnecting means and terminal elements by which energy is transformed to perform a specific function, such as climate control, service water heating, or lighting |
| System Availability | The percentage of time (usually expressed in hours per year) when a photovoltaic system will be able to fully meet the load demand. |
| System Integration (Of New Technologies) | The successful integration of a new technology into the electric utility system by analyzing the technology’s system effects and resolving any negative impacts that might result from its broader use. |
| System Operating Voltage | The output voltage of a solar PV array under load, dependent on the electrical load and size of the battery stack connected to the output terminals. |
| System Storage | See battery capacity. |
Resource Data – Solar Statistic & Data
Wind Resource AssessmentAll markets for wind turbines require an estimate of how much wind energy is available at potential development sites. Correct estimation of the energy available in the wind can make or break the economics of wind plant development. Wind maps developed from the late ’70s to the early ’90s provided reasonable estimates of areas in which good wind resources could be found. Now, new computing tools and new meteorological data sets allow researchers to create even more accurate and detailed wind maps of the world. Wind mapping and validation techniques developed at the NWTC along with collaborations with U.S. companies produce high-resolution maps of the United States that paint a new picture of the wind resource potential. Information System mapping tools and an array of satellite, weather balloon, and meteorological tower data, combined with much-improved numerical computer models provide more data. The higher horizontal resolution of these maps allows for more accurate depiction of the overall wind resource and has led to the identification of new wind development areas where the wind resource was previously considered unsuitable. NWTC provides technical assistance in wind resource assessment including the development and validation of high-resolution wind maps. The focus is to provide the wind industry, policy makers, and other stakeholders with applied wind resource data, information products (e.g., maps), and technical assistance with increasing emphasis on increased heights to effectively evaluate and develop wind potential. For example, a recent project resulted in the development of new wind resource maps at heights of 80 and 100 meters for the contiguous United States and estimates the wind energy potential that would be possible from development of the available windy land area.
The ability to accurately predict when the wind will blow will help remove barriers to wind energy development by allowing wind-power-generating facilities to commit to power purchases in advance. NREL researchers work with federal, state, and private organizations to validate the nation’s wind resources and support advances in wind forecasting techniques and dissemination. Wind resource validation is important for both wind resource assessment and the integration of wind farms into an energy grid. Validating new, high-resolution wind resource maps will provide an accurate reading of the wind resource at a particular site. Development of short-term (1 to 4 hours) forecasting tools will help energy producers proceed with new wind farm projects and avoid the penalties they must pay if they do not meet their hourly generation targets. In addition, validating new high-resolution wind resource maps will give people interested in developing wind energy projects greater confidence as to the level of wind resource for a particular site. |
Resource Data – Solar Statistic & Data
Solar Resource DataThe following solar resource data collections can be found in the Renewable Resource Data Center (RReDC). Cooperative Networks for Renewable Resource Measurements (CONFRRM) Solar Energy Resource Data Historically Black Colleges and Universities Solar Radiation Monitoring Network India Solar Resource Data Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Reduced Circumsolar Radiation Database Measurement and Instrumentation Data Center (MIDC) National Aeronautics and Space Administration Remote Sensing Validation Data National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Solar Data National Renewable Energy Laboratory Spectral Solar Radiation Database National Solar Radiation Database (NSRDB) Solar Energy Measurement Research and Training Sites (SEMRTS) Data Set Solar Resource Variability Data Solar Spectra Typical Meteorological Year Data Sets WEST Associates Solar Monitoring Network |
Resource Data – Solar Statistic & Data
Geothermal MapsThe Geothermal Technologies Office (GTO) carries out R&D and demonstration efforts to deploy 12 GWe of clean geothermal energy by 2020 and expand geothermal into new U.S. regions. Locating and developing resources is an important part of that mission. GTO works with national laboratories to develop maps and data that identify renewable, geothermal resources, possible locations for implementation of various geothermal technologies, and actual and potential geothermal power generation sites. The maps below were developed by National Laboratories, universities and other organizations. Maps by Energy Type or Measurement
Maps by LocationU.S. and North America
States and Regions
Global
|
Resource Data – Solar Statistic & Data
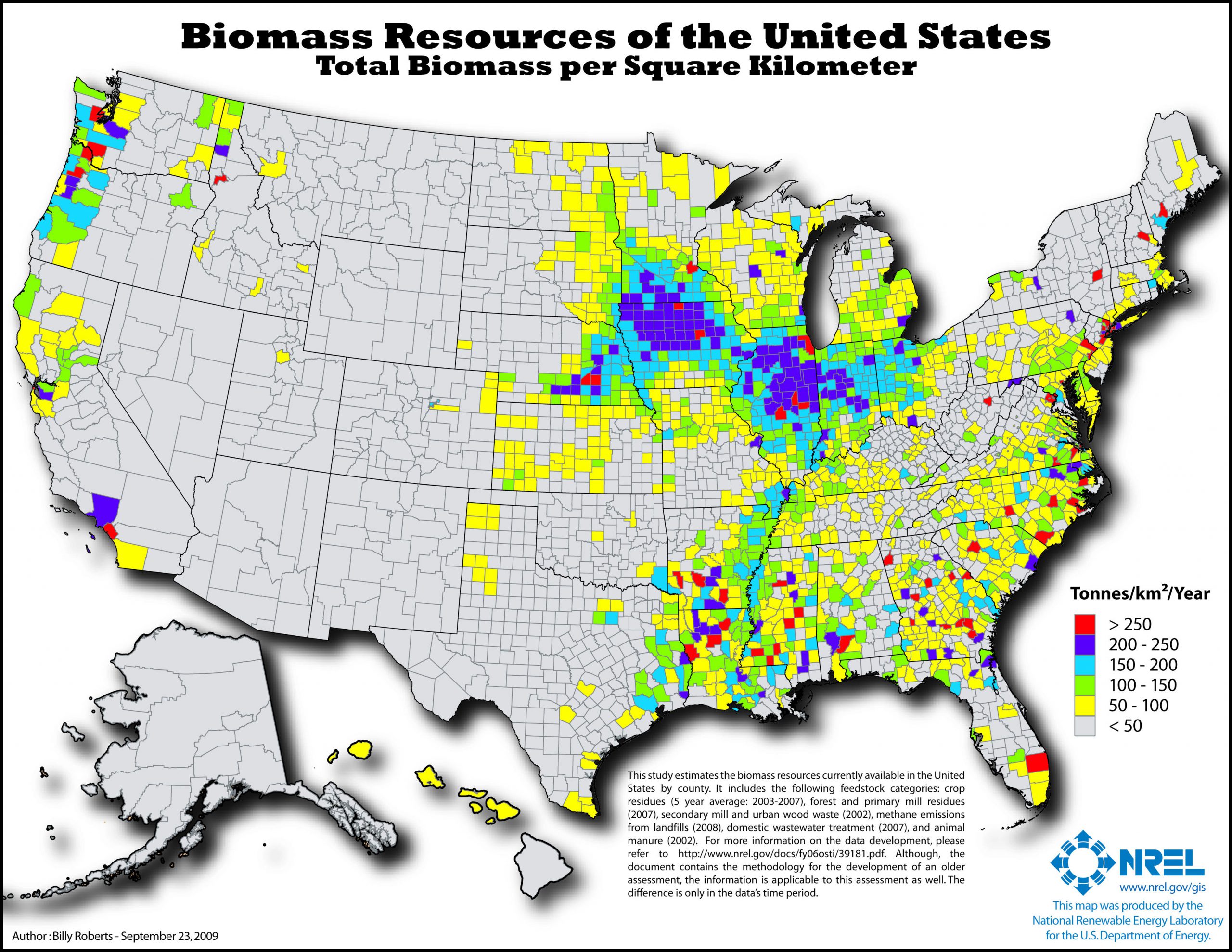
Biomass MapsThese maps illustrate the biomass resources available in the United States by county. Biomass feedstock data are analyzed both statistically and graphically using a geographic information system (GIS). The following feedstock categories are evaluated: crop residues, forest residues, primary and secondary mill residues, urban wood waste, and methane emissions from manure management, landfills, and domestic wastewater treatment. Biomass Resources in the United States Total Resources by County – Total Biomass per Square Kilometer – These maps estimate the biomass resources currently available in the United States by county. They include the following feedstock categories: crop residues (5 year average: 2003-2007) forest and primary mill residues (2007), secondary mill and urban wood waste (2002), methane emissions from landfills (2008), domestic wastewater treatment (2007), and animal manure (2002). For more information on the data development, please refer to https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy06osti/39181.pdf Crop residues – The following crops were included in this analysis: corn, wheat, soybeans, cotton, sorghum, barley, oats, rice, rye, canola, dry edible beans, dry edible peas, peanuts, potatoes, safflower, sunflower, sugarcane, and flaxseed. The quantities of crop residues that can be available in each county are estimated using total grain production, crop to residue ratio, moisture content, and taking into consideration the amount of residue left on the field for soil protection, grazing, and other agricultural activities. Source: USDA, National Agricultural Statistics Service; five-year average: 2003-2007. Forest residues – This category includes logging residues and other removable material left after carrying out silviculture operations and site conversions. Logging residue comprises unused portions of trees, cut or killed by logging and left in the woods. Other removable materials are the unutilized volume of trees cut or killed during logging operations. Source: USDA, Forest Service’s Timber Product Output database, 2007. Primary mill residues – Primary mill residues include wood materials (coarse and fine) and bark generated at manufacturing plants (primary wood-using mills) when round wood products are processed into primary wood products, such as slabs, edgings, trimmings, sawdust, veneer clippings and cores, and pulp screenings. Source: USDA, Forest Service’s Timber Product Output database, 2007. Secondary mill residues – Secondary mill residues include wood scraps and sawdust from woodworking shops — furniture factories, wood container and pallet mills, and wholesale lumberyards. Data on the number of businesses by county was gathered from the U.S. Census Bureau, 2009 County Business Patterns. Urban wood waste Methane emissions from landfills – The methane emissions are estimated for each landfill considering total waste in place, landfill size, and location (arid or non-arid climate), and then aggregated to county level. Note: this dataset doesn’t include all landfills in the United States due to gaps in either precise geographic location or waste in place. Source: EPA, Landfill Methane Outreach Program (LMOP), April 2008. Methane emissions from manure management – The following animal types were included in this analysis: dairy cows, beef cows, hogs and pigs, sheep, chickens and layers, broilers, and turkey. The methane emissions were calculated by animal type and manure management system at a county level. Source: USDA, National Agricultural Statistics Service, 2002 data. Methane emissions from domestic wastewater treatment – The methane emissions are estimated using the methodology from the EPA Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2003. Source: U.S. Census Bureau, 2007 County Population. |
Useful Reference Materials
| Calculator links | |||
|
|||
|
more Calculators links |
|||
| Case Study links | |||
|
|||
|
more Case Studies links |
|||
| Map links | |||
|
|||
|
more Maps links |
|||
| Product & Service links | |||
|
|||
| Statistic links | |||
|
|||
|
more Statistics links |
Useful Reference Materials
| Calculator links | ||||
|
||||
|
more Calculators links |
||||
| Case Study links | ||||
|
||||
|
more Case Studies links |
||||
| Map links | ||||
| Renewable Energy Maps | ||||
| Product & Service links | ||||
|
||||
| Statistic links | ||||
|
DSE Energy Glossary
|
DSE Energy Glossary
| Quad | One quadrillion Btu (1,000,000,000,000,000 Btu). |
| Qualification Test | A procedure applied to a selected set of photovoltaic modules involving the application of defined electrical, mechanical, or thermal stress in a prescribed manner and amount. Test results are subject to a list of defined requirements. |
| Qualification Test (PV) | A testing procedure for PV modules relating to electrical, mechanical, or thermal stress. |
| Qualifying Facility | A cogenerator or small power producer which under federal law, has the right to sell its excess power output to the public utility. |
| Qualifying Facility (Qf) | Under PURPA, QFs were allowed to sell their electric output to the local utility at avoided cost rates. To become a QF, the independent power supplier had to produce electricity with a specified fuel type (cogeneration or renewables), and meet certain ownership, size, and efficiency criteria established by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. |
| Quartz-Halogen Light | An incandescent lamp filled with halogen gas. Somewhat more efficient than standard incandescents. |
| Quasi Sine-Wave | A description of the type of waveform produced by some inverters. |